%%{
init: {
'theme': 'base',
'flowchart': { 'curve': 'natural' }
}
}%%
flowchart LR
T(Theory)
P(Phenomena)
D(Data)
T -- "Explanation" --> P
P -- "Abduction" --> T
P -- "Prediction" --> D
D -- "Generalization" --> P
What are (Not) Theories & Models?
What is a theory?
Like so many words that are bandied about, the word theory threatens to become meaningless. Because its referents are so diverse - including everything from minor working hypotheses, through comprehensive but vague and unordered speculations,to axiomatic systems of thought - use of the word often obscures rather than creates understanding.Merton (1967, p. 39)
Maybe an easier question for the start: What is not a theory?
What is not a theory?
1. References To Theory Are Not Theory
(Note: While the following features of a scholarly article do not constitute a theory, they might be important in their own right)
A manuscript that Robert Sutton edited had strong data, but all three reviewers emphasized that it had “weak theory” and “poorly motivated hypotheses.” The author responded to these concerns by writing a new introduction that added citations to many papers containing theory and many terms like “psycho-social theory,” “identity theory,” and “social comparison theory.”
But it still contained no discussion of what these theories were about and no discussion of the logical arguments why these theories led to the author’s predictions. The result was that this paper contained almost no theory, despite the author’s assertion that much had been added.
Solution:
Authors need to explicate which concepts and causal arguments are adopted from cited sources and how they are linked to the theory being developed or tested.
What is not a theory?
2. Data Are Not Theory
Empirical evidence plays an important role in confirming, revising, or discrediting existing theory and in guiding the development of new theory. But observed patterns like beta weights, factor loadings, or consistent statements by informants rarely constitute causal explanations.
Kaplan (1964) asserted that theory and data each play a distinct role in behavioral science research: Data describe which empirical patterns were observed and theory explains why empirical patterns were observed or are expected to be observed.
In our words: Repeated patterns in data establish phenomena. They do not explain them.
What is not a theory?
3. Lists of Variables or Constructs Are Not Theory
Papers […] often are written as if well-defined variables or constructs, by themselves, are enough to make theory. Sometimes the list of variables represents a logical attempt to cover all or most of the determinants of a given outcome or process.
Such lists may be useful catalogs of variables that can be entered as predictors or controls in multiple regression equations […], but they do not constitute theory.
Notes:
- Lists of constructs (without an explicit definition of their causal relationship) often are called a framework.
- When we build our models, we will also create tables of constructs and variables. But that alone is not yet a theory!
What is not a theory?
4. Diagrams (Alone) Are Not Theory
4. Diagrams (Alone) Are Not Theory
4. Diagrams (Alone) Are Not Theory
4. Diagrams (Alone) Are Not Theory
What is not a theory? 4
4. Diagrams (Alone) Are Not Theory
Diagrams or figures can be a valuable part of a research paper but also, by themselves, rarely constitute theory. […]
More helpful are figures that show causal relationships in a logical ordering, so that readers can see a chain of causation or how a third variable intervenes in or moderates a relationship. Also useful are temporal diagrams showing how a particular process unfolds over time. […]
As Whetten (1989) suggested, while boxes and arrows can add order to a conception by explicitly delineating patterns and causal connections, they rarely explain why the proposed connections will be observed. Some verbal explication is almost always necessary.
Discussion: Are then VAST displays on their own sufficient to constitute a theory?
No, because they do not present arguments why a certain causal path (or other elements) should exist.
What is not a theory?
5. Hypotheses (or Predictions) Are Not Theory.
Hypotheses can be an important part of a well-crafted conceptual argument. They serve as crucial bridges between theory and data, making explicit how the variables and relationships that follow from a logical argument will be operationalized. […]
Hypotheses do not (and should not) contain logical arguments about why empirical relationships are expected to occur. Hypotheses are concise statements about what is expected to occur, not why it is expected to occur.
But, then:
What is a theory?
Theories as causal explanations
“It may be said… that an explanation is not fully adequate unless its explanans […] could have served as a basis for predicting the phenomenon under consideration.
… not merely to record the phenomena of our experience, but to learn from them, by basing upon them theoretical generalizations which enable us to anticipate new occurrences and to control, at least to some extent, the changes in our environment”Hempel & Oppenheim, 1948, (p. 138)
Put in other words: Explanatory theories aim at causal/mechanistic understanding that supports prediction and, under suitable scope conditions, control.
TCM: A methodology for constructing theories
Phenomena: Stable and general features of the world in need of explanation. Can be understood as robust generalizations of patterns in empirical data. They are the explanatory targets for scientific theories (the explanandum). In psychology often called “effects”.
Data: Relatively direct observations. Refer to particular empirical patterns in concrete data sets rather than empirical generalizations (which would be phenomenona).
Explanatory Theories are constructed to explain the empirical phenomena that are evidenced by data (i.e., they are the explanans). Explanatory theories can be expressed in terms of a set of linked propositions referring to latent psychological constructs. At least one of these propositions expresses a general principle.
Definitions (1)
A theory is a set of statements about the relationship(s) between two or more constructs with a nomological (i.e. law-like) character. (explanans)
Dissecting the dense definition:
- Theories are not about specific measurements or operationalizations: they are about (a) latent constructs, and (b) explains phenomena (generalizable patterns in data).
- “Statements”: Typically these are causal statements (if-then), but the definition is broad and includes also other statements (e.g., correlational).
What is a model?
A {formal|mathematical|computational} model is a precise, mathematical or algorithmic representation of the theory’s principles and relationships. It serves as a bridge between abstract theoretical principles and the empirical world.
As theories are about constructs, there is a gap between theory and implemented models: We need more assumptions to implement a model in computer code and to make it empirically testable. These are typically assumptions about operationalization (how to measure constructs) and auxiliary assumptions (additional assumptions that are not part of the core theory, but are needed to implement it, such as specific functional forms).
Filling the gaps between theory and implemented model is called model specification. There is no 1-to-1 mapping of a theory to a derived model: Multiple models can satisfy the axioms and constraints of a theory.
Explicating a verbal theory into formal model(s)
Example: van Dongen et al (2023) on Ego Depletion
- The regulatory resource theory pertains to self-control: cognitive processes that inhibit and suppress immediate thoughts, impulses, expression of emotions, and behaviors that deviate from standards or goals.
- The theory postulates that one’s ability for self-control depends on a finite resource: a stored supply of energy, for which some use the term willpower. Every act of self-control reduces the amount of willpower, so that one’s ability to inhibit or suppress the next unwanted impulse is diminished
- The theory is said to explain the phenomenon of ego depletion: people perform worse on a task that requires self-control, right after having done something else that used this resource.
Explicating a formal theory into formal model(s)
Key theoretical principles of the verbal theory
- there is a domain-general “resource” called willpower (\(W\))
- tasks requiring willpower deplete this resource (e.g., a task that requires self-control depletes the resource, but a task that requires no self-control does not), and
- the resource is replenished at some rate after the task ends.
To these, we add the following auxiliary assumptions:
- willpower \(W\) is a positive valued quantitative variable (\(W \in \mathbb{R}^{+}\))
- willpower changes continuously in time, and
- willpower has a default value when at rest ( i.e., when there is no task that requires willpower; \(W^r\)).
Explicating a formal theory into formal model(s)
Multiple possible implementations
The theoretical key principles are not precise enough yet to program an implementation - e.g.: Is the decrease of the resouce linear or curved? How fast does the resource recover under rest?
These additional auxiliary assumptions (which are not in the core of the theory) can lead to very different possible implementations - all of which are compatible with the theory:
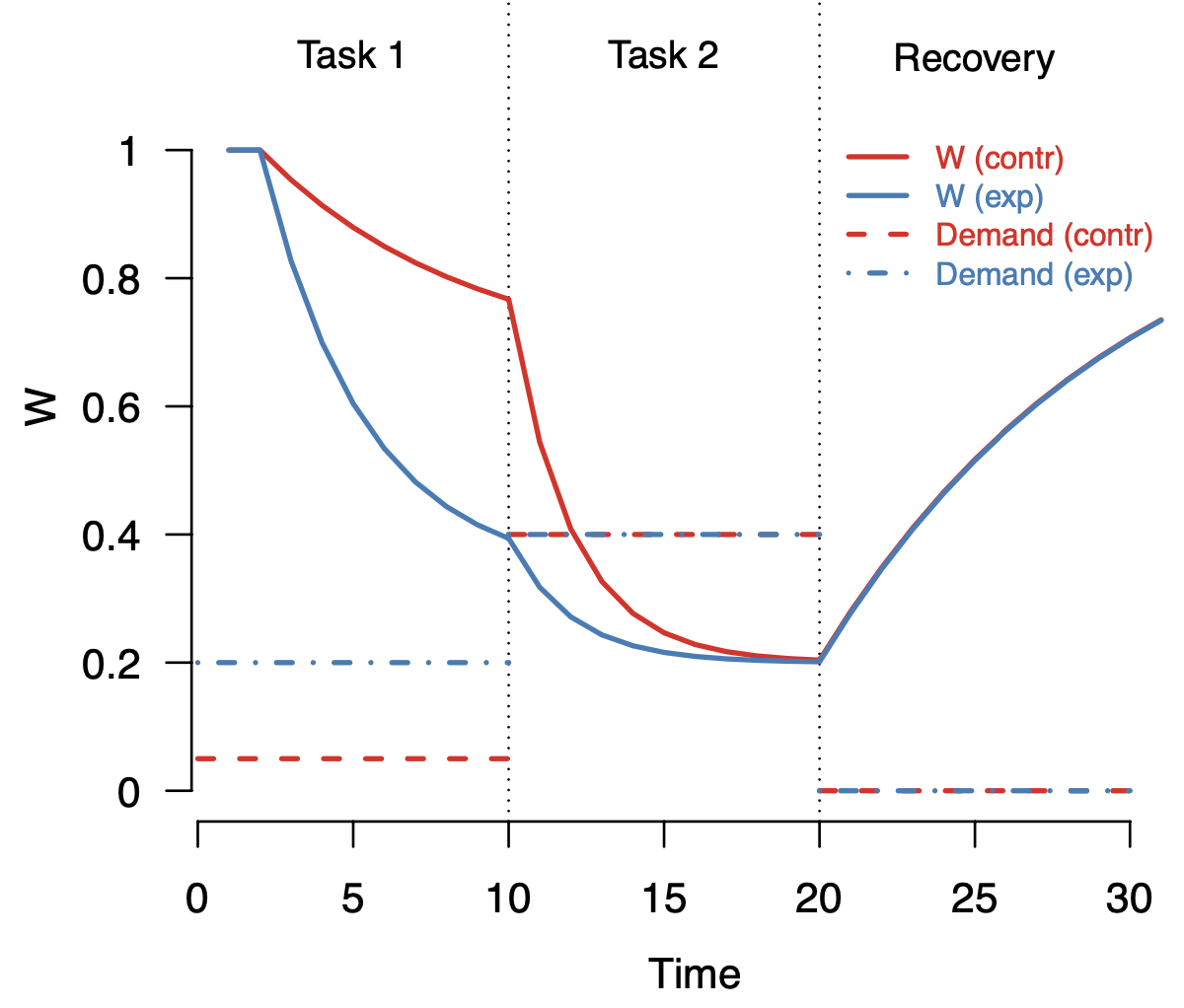
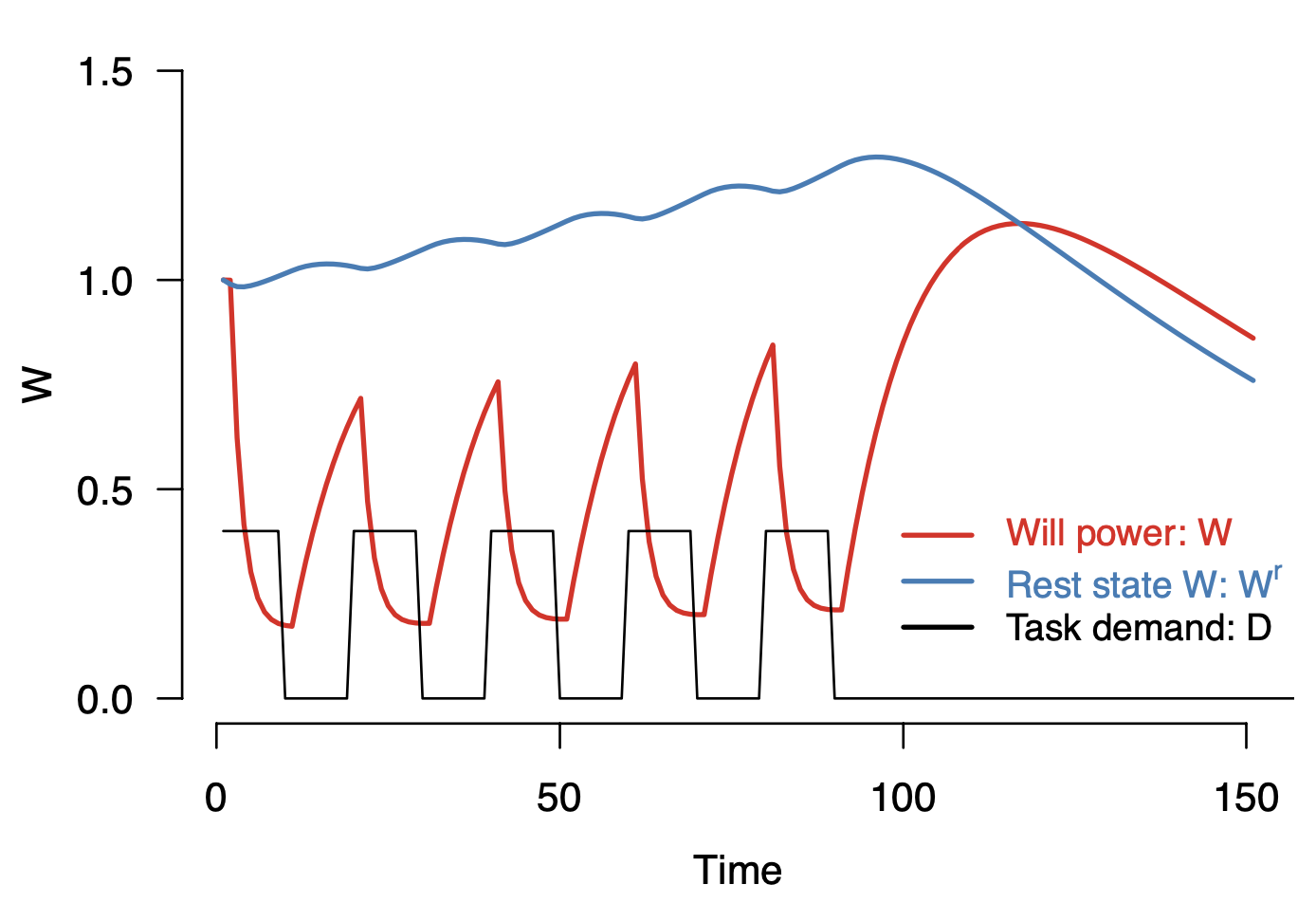
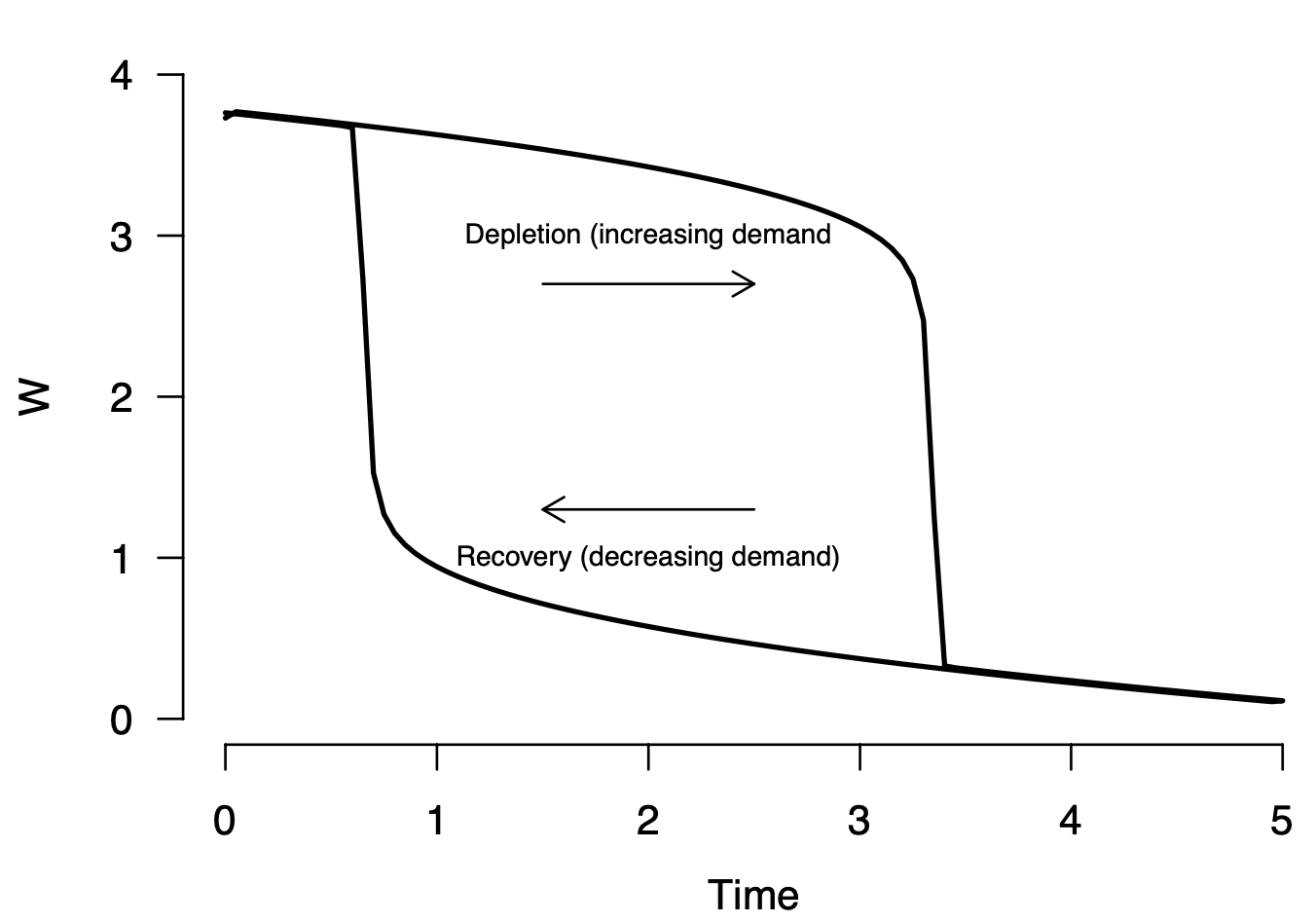
Narrative - theory - model
“Die Aura des assoziativ Mitgedachten”
In der sozialwissenschaftlichen Literatur finden sich oft Argumente, die gegen eine Formalisierung sprechen, wie z.B. die folgende Bemerkung: “Was bei der Formalisierung notwendig verloren geht, ist die Aura des assoziativ Mitgedachten, die verbale Aussagen stets umgibt, über ihren ausdrücklichen Gehalt hinaus mit Wirklichkeit sättigt und auch in Grenzfällen noch zutreffend erscheinen lässt” (Mayntz 1967: 28, vgl. auch Harbordt 1974:271).
Solche Kritikpunkte können wir nicht nachvollziehen. (…) Wenn man daran interessiert ist, “die Aura des assoziativ Mitgedachten” zu erhalten, ist schöngeistige Literatur ein geeigneteres Betätigungsfeld als Wissenschaft.
(Manhart, 2007)
Narrative - theory - model
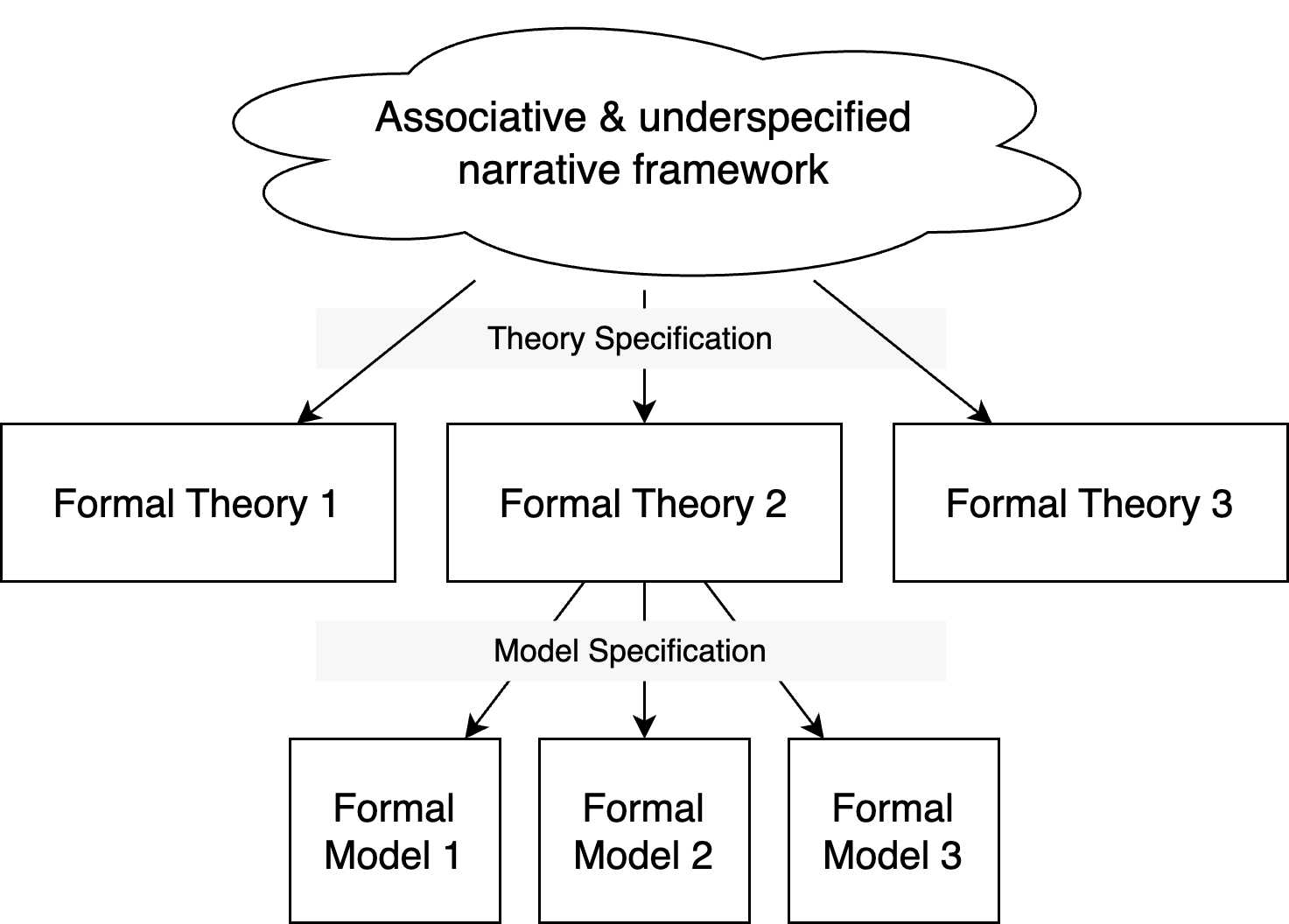
Narrative - theory - model
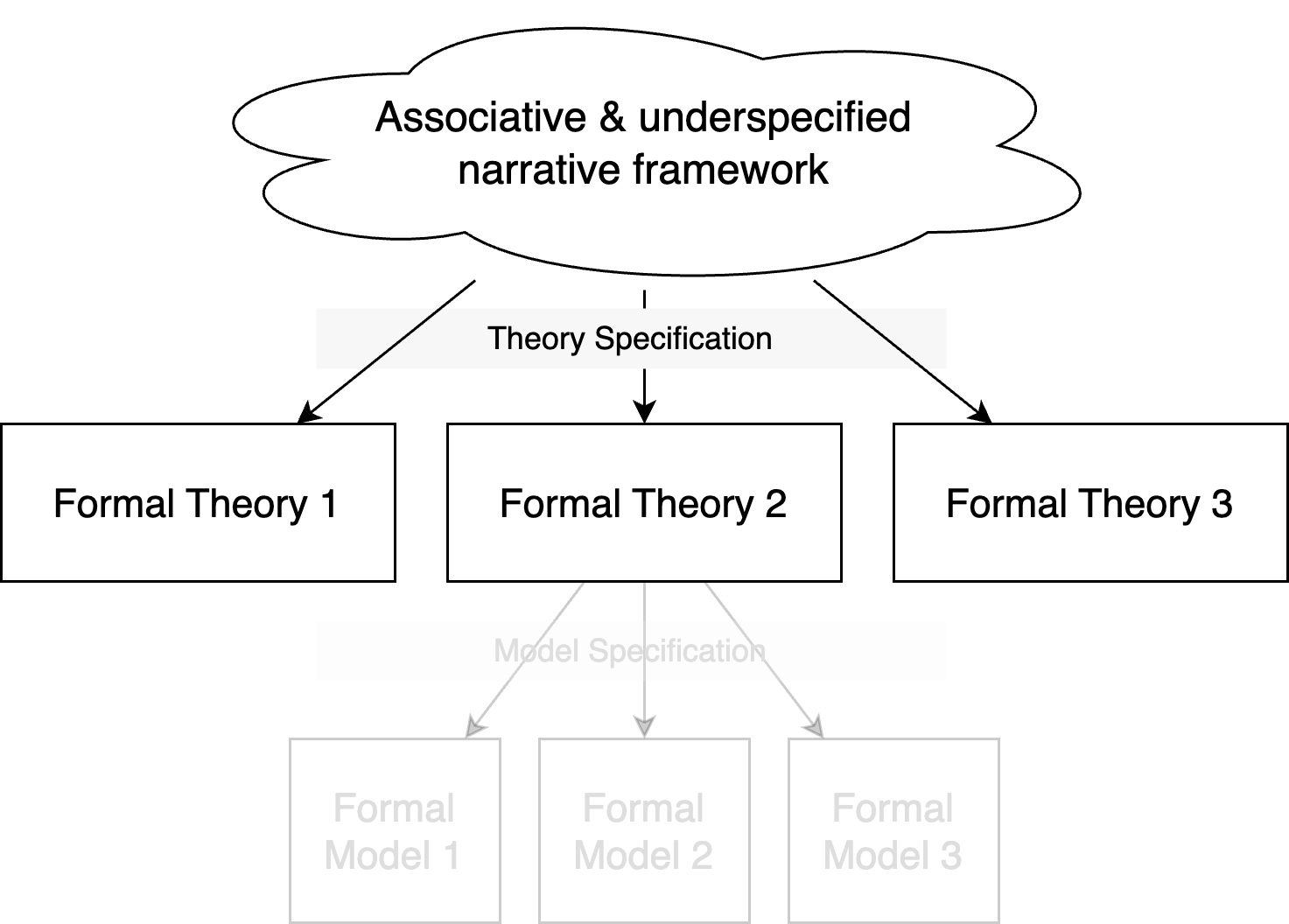
Theory Specification: Deriving a precise formal theory from a narrative framework
- Multiple formal theories can be derived from a narrative framework
- Even if they are all compatible with the narrative framework, they can be mutually incompatible.
- Or they can be complementary (e.g., referring to different domains, or covering different aspects of the narrative framework), e.g. evolution as framework
Narrative - theory - model
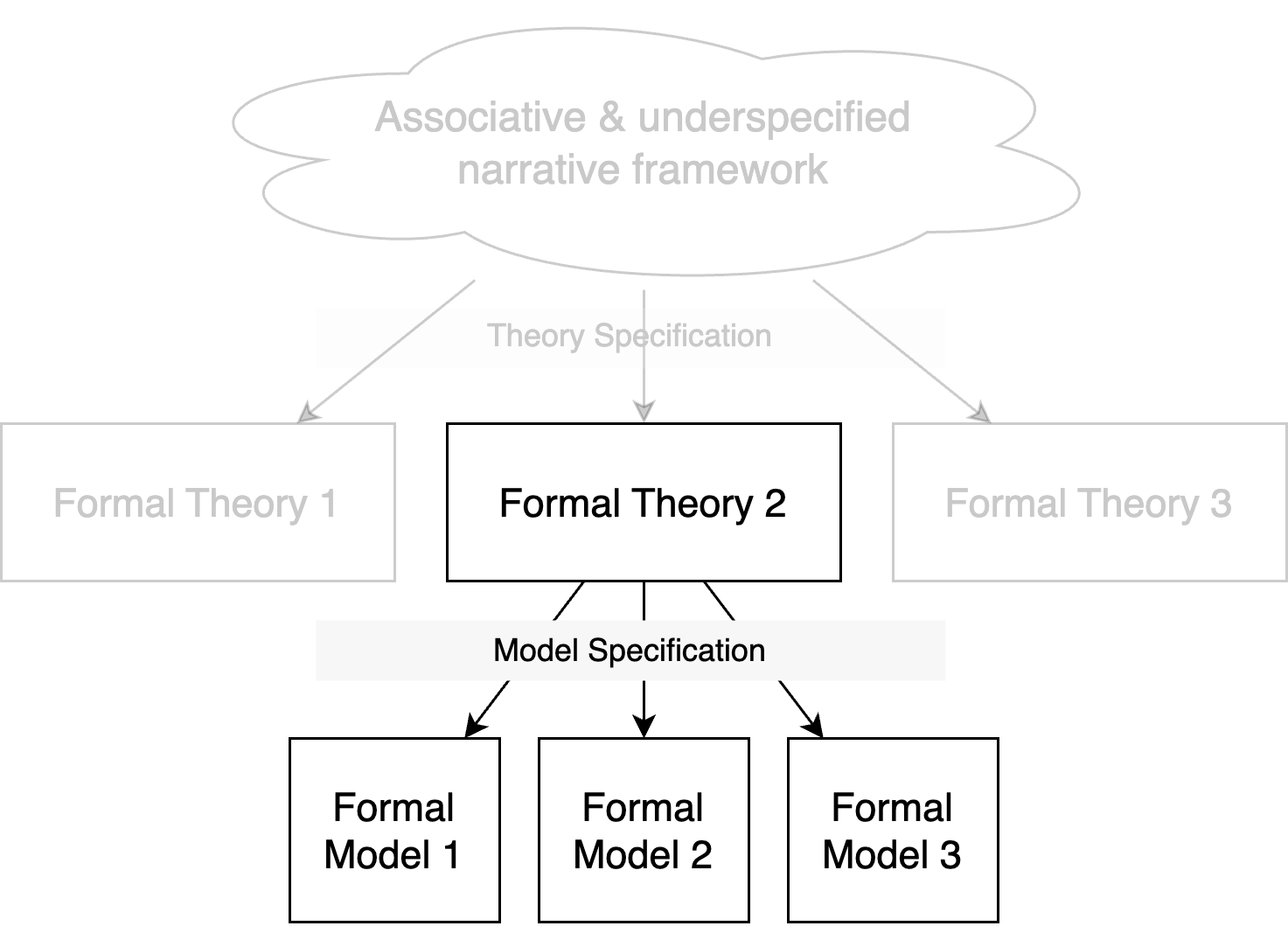
Model Specification: Deriving a precise formal model from a theory
- Multiple formal models can be derived from a single theory
- Even if they are all compatible with the theory, they can be mutually incompatible due to different auxiliary assumptions.
- A generative model is so precise (and fully specified) that it can be used to generate “fake” data.
- Even if the concrete numerical predictions will differ, all admissible models should satisfy the theory’s core qualitative predictions within its scope (e.g., direction of effects, monotonicity)
What then are explanations?
With the definition of explanatory theories and formal models, a definition of explanations can be proposed:
“Theory T putatively explains phenomenon P” means:
“if the world were as T says it is, P would follow as a matter of course.”
Although this notion of explanation is arguably incomplete, it has the advantages of being close to the commonsense understanding of the concept and being easy to implement in a formal model—namely by creating a virtual world in which theory T is true and showing that this world will indeed produce phenomenon P.
Understandability of explanations
Farrell & Lewandowsky (2018), referring to Trout (2007), emphasize the understandability of explanations:
- Explanations can “be epistemically valuable only if we could, implicitly or explicitly, understand them. As a result, explanation must maintain some contact with our psychological powers of understanding” (Trout, 2007, p. 565)
- “an explanation that cannot be understood is not an explanation”
- “some facts of the universe may remain irreducibly mysterious to humans - not because explanations do not exist in principle but because they cannot be humanly understood and hence cannot be formulated”
- “models in psychology benefit from simplifying the reality they seek to explain even though this simplification would likely render the model wrong. At the risk of being provocative, we would even argue that models are useful only because they are wrong.” (cf. von Uexküll!)
Definitions (2)
A theory is a set of statements about the relationship(s) between two or more constructs with a law-like character.
A model is a precise mathematical or computational instantiation of some theory claims plus operationalizations and auxiliary assumptions. It is able to generate “fake” data and data patterns that would be observed in reality if the theory and the model are sufficiently accurate.
In the productive explanation framework, a theory \(T\) putatively explains a phenomenon \(P\) if and only if a formal model \(M\) of the theory \(T\) produces a statistical pattern representing the empirical phenomenon \(P\).
%%{
init: {
'theme': 'base',
'flowchart': { 'curve': 'natural' }
}
}%%
flowchart LR
T(Theory)
P(Phenomena)
D(Data)
M(Model)
T -- "Explanation" --> M
M -- "Explanation" --> P
P -- "Abduction" --> T
P -- "Prediction" --> D
D -- "Generalization" --> P
